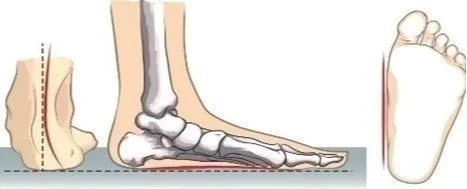
WHAT IS PEDIATRIC FLATFOOT?
Flatfoot is common in both children and adults. When this deformity occurs in children, it is referred to as pediatric flatfoot. Although there are various forms of flatfoot, they all share one characteristic - partial or total collapse of the arch.
Pediatric flatfoot can be classified as symptomatic or asymptomatic. Symptomatic flatfeet exhibit symptoms, such as pain and limitation of activity, while asymptomatic flatfeet show no symptoms. These classifications can assist your sports medicine podiatry specialist determine an appropriate treatment plan.
Symptoms
Flatfoot can be apparent at birth or it may not show up until years later. Most children with flatfoot have no symptoms, but some may have one or several symptoms. Some symptoms a child may experience are pain, tenderness, or cramping in the foot, leg, or knee. They may also notice decreased energy in wanting to participate in any physical activities or even total withdrawal from any activity. Another symptom is outward tilting of the heel resulting in awkwardness or a change in a child’s walking.
Professional treatment of flatfeet will depend on the severity and cause of the problem. It’s vital to have flatfeet examined by a podiatrist because it can lead to more serious problems like heel spurs, ankle, or knee pain, or arthritis.
If you or someone that you care for suffers from pain in the feet, ankles, knees, hips, and/or lower back, the pain may be due to misalignment caused by faulty biomechanics (such as flatfeet) which can be treated and corrected with the help of custom orthotic insoles. To schedule your comprehensive biomechanical evaluation, use our contact form or call our Sports Medicine Podiatry Center and book an appointment at our Cherry Hill, N.J. Sports Medicine Facility or Ridley Park, P.A. Office location with one of our podiatric sports medicine specialists today by calling (610) 522-9200.